How a Power Audit Works
How a Power Audit Works
With SyAM Management Utilities and Power Auditor, IT administrators can identify cost savings to be achieved through power management. SyAM Management Utilities and Power Auditor collect data on the actual number of hours that machines are powered on. Savings are calculated based on the desired power on/off hours, with configurable settings for power consumption and cost. The power management features of Management Utility are used to enforce the desired policies, and achieved savings are calculated.
The first part of the process is collecting the data. Systems are discovered on the network, and organized into groups. For each group of systems a range of hours is defined to specify the time those systems are expected to be powered on, and when they are normally shut down. This specification is called a Power On Hours template.
During the data collection phase, the Power Auditor is in Identified Savings mode. When we calculate Identified Savings, we compare the number of hours that a system is actually powered on with the number of hours we would like it to be running. Power Auditor provides default settings for system and monitor wattage consumption, as well as power cost per kilowatt hour. The IT manager can override these settings to improve the accuracy of calculated savings.
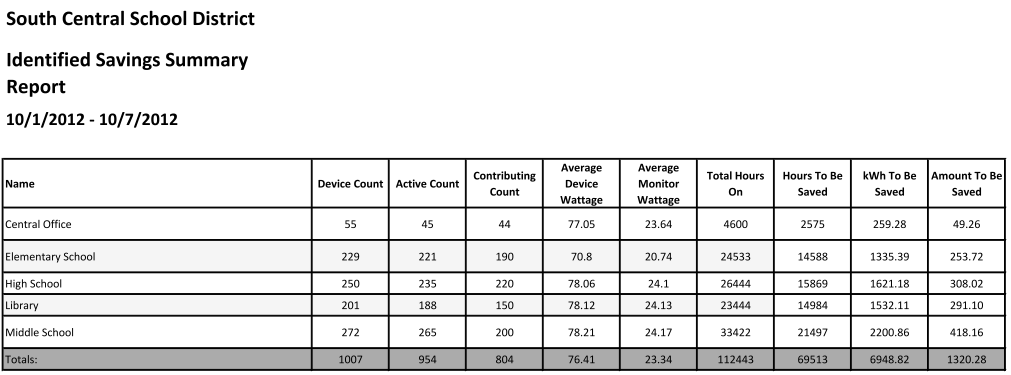
Identified savings reports contain the following information (per group and totals):
- Name: The name of the Power Audit group
- Device Count: Total number of systems in the group
- Active Count: The number of systems that reported powered on status at any time during the reporting period
- Contributing Count: The number of systems that contributed to identified savings, that is, they were powered on for more hours than specified by the Power On Hours template
- Average Device Wattage: System power consumption as specified in the Power On Hours template
- Average Monitor Wattage: Display power consumption as specified in the Power On Hours template
- Total Hours On: Number of powered on hours for the entire group during the reporting period
- Hours To Be Saved: Number of powered on hours outside those specified by the Power On Hours template
- kWh To Be Saved: Total potential power saving for the group, based on wattages and hours calculated
- Amount To Be Saved: Total potential money saved for the group, based on kWh savings calculated and cost per kWh specified in Administration Settings
At a minimum, we collect seven full days of system power-on data, to establish a baseline before any action is taken to enforce power management settings.
Once the baseline of data has been collected, we can move into Achieved Savings mode. Using the Management Utility along with SyAM System Client and SyAM System Area Manager, we apply Power Management settings to the systems so they will be powered off at a desired time for each day of the week. Settings can be configured to protect against system shutdown while a user is active, or when a particular program is in use.
Achieved Savings is calculated by comparing the actual powered on hours with the baseline of data that was collected during the Identified Savings period, before power management was implemented. The result is a report of what has actually been saved by enforcing power management policies.
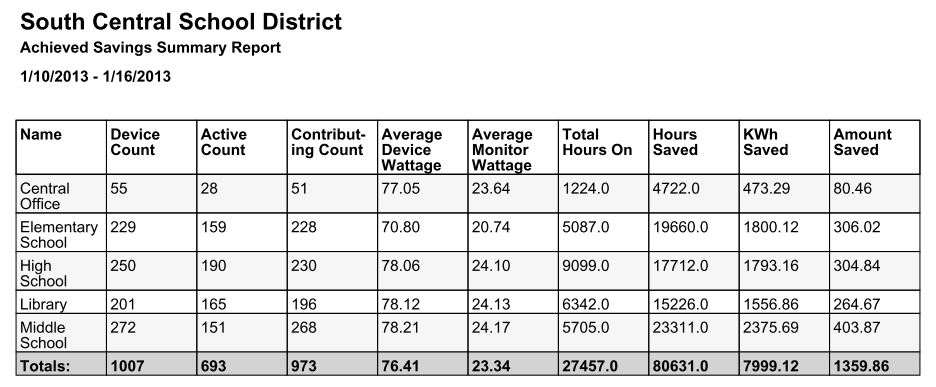
Achieved Savings reports contain some of the same information as Identified Savings reports, but there are some differences:
- Contributing Count: The number of systems that contributed to achieved savings, that is, they were powered on fewer hours than the baseline average
- Hours Saved: Number of powered on hours saved through power management, compared with the baseline data
- kWh Saved: Actual power saving for the group, based on wattages and hours calculated
- Amount Saved: Actual money saved for the group, based on kWh savings calculated and cost per kWh specified in Administration Settings
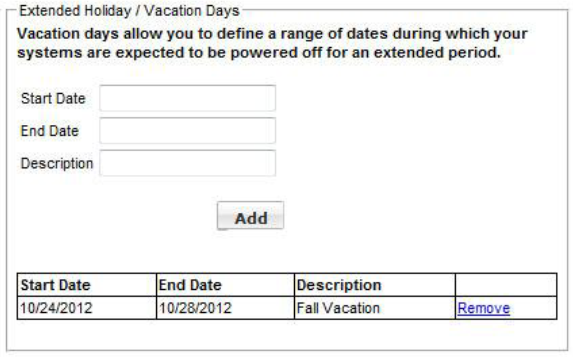
Extended Holidays/Vacation Days
For holidays and vacation periods you can set a range of dates in Extended Holiday/Vacation Days. On any day specified here, a system that is powered off all day will not be included in savings calculations. A system that is powered on for any part of the day will be included.
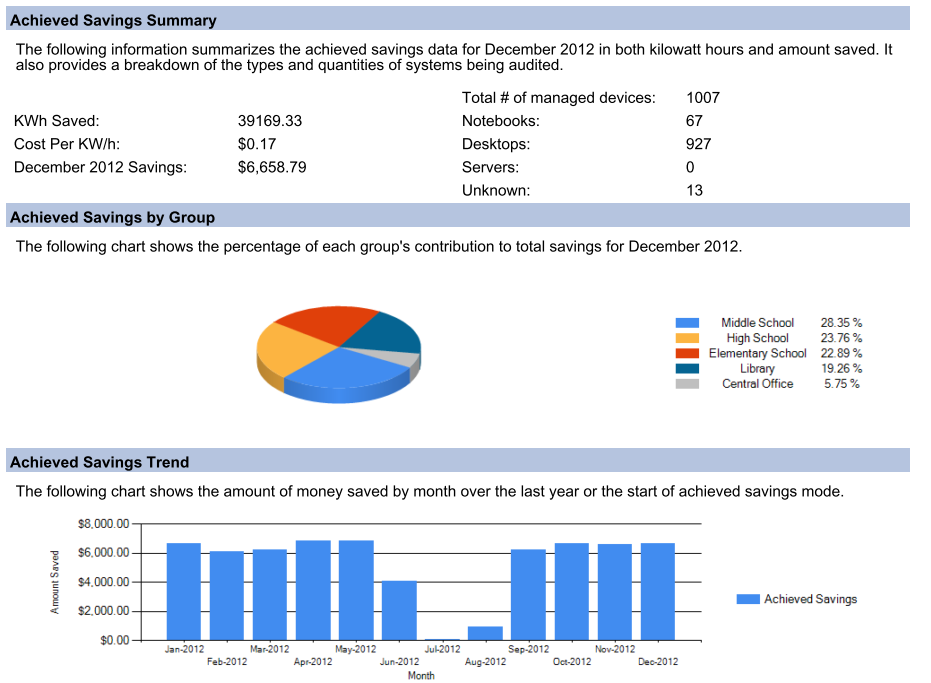
Once in achieved savings mode and fully deployed with the SyAM Software solution a monthly Executive level report is available. This report provides an easy to read graphically representation on how well the organization is doing on power savings.
The Executive Report summarizes achieved savings results;
- For the selected month in detail
- Prior year totals,
- Displays savings by group
- 12 Month trend in amount of money saved
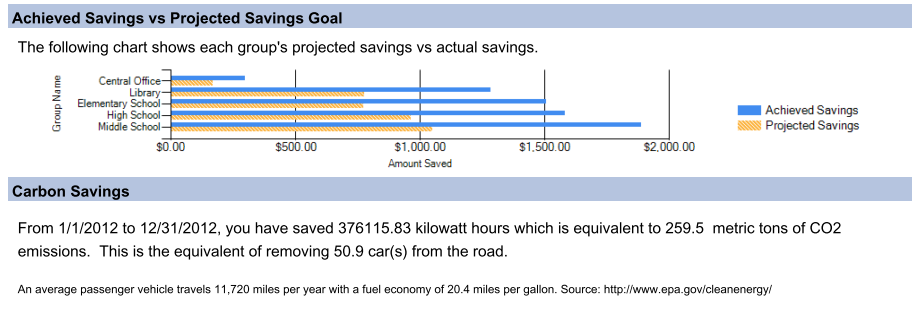
- Comparison of achieved savings with projected savings by group
It can be automatically emailed at the start of each month and produced in HTML or PDF format on demand.
A power audit will create an accurate baseline to report exactly how many killowatts are used on a regular basis. This baseline is then compared to the power management polices that would be implemented. By creating an accurate baseline of current power consumption, and comparing that to what should be saved in the future after activating power management policies, we can present you with an achieved vs projected savings chart. This chart will compare how much you planned on saving vs how much you actually have saved. In some cases companies save even more than expected. An example is on page 6.
The baseline from the power audit is based off of a variety of data points:
- Number of hours that could be saved = Number of hours identified as powered on when not needed.
- Idle wattage per system = Wattage consumption of PC in idle mode (Can be entered manually)
- Kilowatts identified to be saved = (A x B) /1000
- Cost per kilowatt (Varies by location)
- Projected savings per week per system = C x D
- Number of systems in group = Total systems audited by SyAM
- Projected savings for group per week = E x F
- Average Projected Savings per day = G / 7 (days of the week)
- Projected Savings for the month = H x number of days in month